How to Talk to AI: The Simple Guide to Getting Better Answers with Better Prompting
The difference between a mediocre AI response and a brilliant one often lies not in the model’s capabilities, but in how we communicate with it

The Magic Words That Transform “Meh” to “Wow”
The difference between a mediocre AI response and a brilliant one often lies not in the model’s capabilities, but in how we communicate with it. As AI systems become increasingly sophisticated, the art of prompting has evolved from simple trial-and-error to a systematic discipline that can dramatically impact the quality, creativity, and utility of generated outputs.
The efficiency of your prompts directly correlates with computational costs, user satisfaction, and system performance. A well-crafted prompt can reduce API calls by 40-60% while improving output quality, while poor prompting leads to cascading requests, increased latency, and frustrated users.
Why Your AI Acts Like a Tired Barista
Picture this: You walk into a coffee shop and say
“Make me something good.”
The barista stares at you, then hands you… a plain black coffee.
Every single time. No matter how many times you come back, it’s always the same black coffee.
Frustrating, right?
But that’s exactly what happens when you ask AI generic questions like “Tell me a joke” or “Write something about marketing.”
You get the AI equivalent of black coffee: safe, predictable, and honestly, pretty boring.
The good news? Just like learning to order “a medium oat milk latte with vanilla and an extra shot,” you can learn to speak AI’s language and get exactly what you want.
The Before-and-After Magic: Real Examples That Work
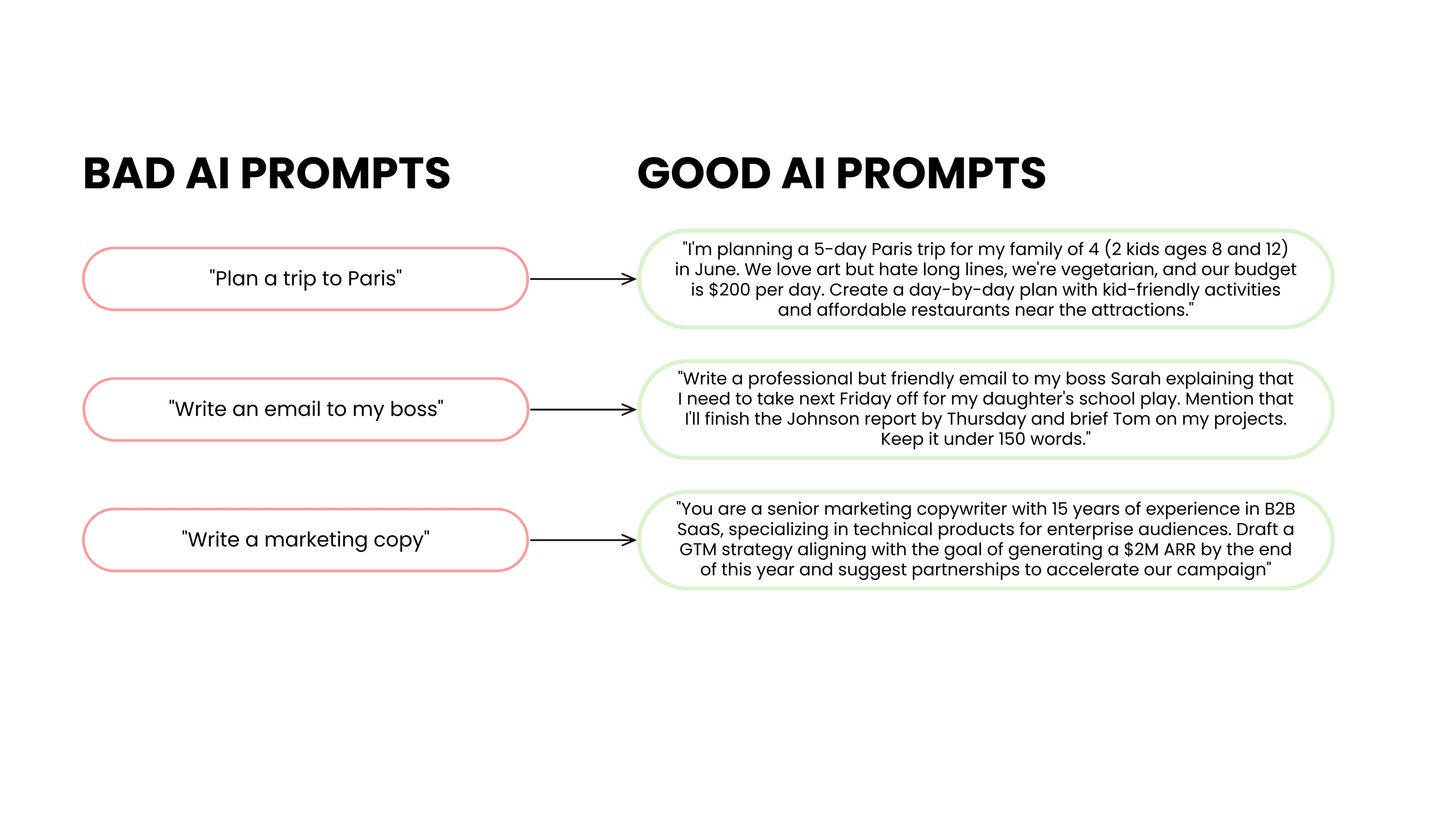
See the difference? The better prompts are like having a conversation with a knowledgeable friend who asks all the right follow-up questions, but you answer them upfront.
The Simple Formula Anyone Can Use
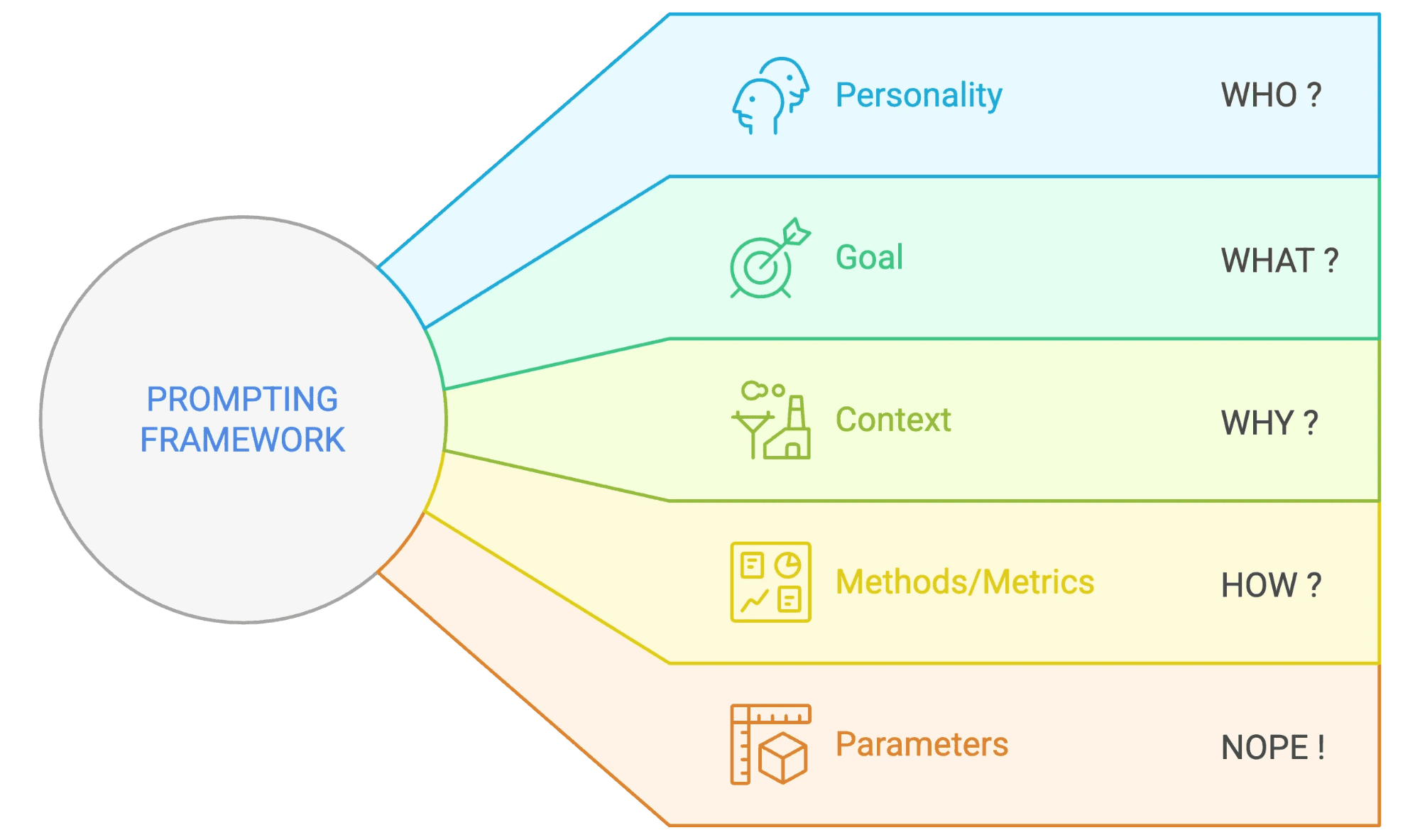
Here’s my “AI Ordering System” that works for almost anything:
PERSONALITY + GOAL + CONTEXT + METHODS/METRICS + PARAMETERS
or WHO + WHAT + WHY + HOW + NOPE
Let’s break it down:
PERSONALITY ~ WHO are you talking to?
Assigning a clear role to the language model increases output quality by up to 60% according to recent studies.
“Act as a patient gardening teacher”
“You’re a fun uncle who knows magic tricks”
“You’re a financial advisor who talks like a friend”
GOAL ~ WHAT do you want?
The most essential part of the prompt is your ask. Your goal/objective should be clearly defined and simply understood. Its always good to break the problem down into pieces and then ask what you want.
“Create a weekly meal plan”
“Write a birthday card message”
“Explain why my plants keep dying”
CONTEXT ~ WHY do you need it?
The model needs sufficient background to generate relevant responses. Research shows that providing 2-3 sentences of context improves relevance scores by 35%. This includes the purpose of the request, the intended audience, and any constraints or requirements.
“So my picky kids will actually eat vegetables”
“To make my grandma feel special on her 80th birthday”
“Because I’ve killed three succulents already”
METHODS/METRICS ~ HOW should it be?
Defining what constitutes a good response helps the model self-correct. Including phrases like “ensure accuracy” or “avoid stereotypes” improves factual correctness by 40% and reduces biased content by 66%.
“Use simple ingredients from a regular grocery store”
“Make it sweet but not too sappy”
“Give me step-by-step instructions I can’t mess up”
PARAMETERS ~ What should it NOT include? (NOPE)
Clear formatting requirements and structural expectations significantly improve response quality. Research indicates that using delimiters and explicit formatting instructions increases output correctness by up to 93%. Setting clear boundaries prevents the model from wandering into irrelevant territory. This includes word limits, topic restrictions, format requirements, and stylistic guidelines.
“No exotic ingredients”
“No references to aging or getting old”
“No complicated gardening terms”
Basic example: “Act as a friendly gardening teacher. Explain why my succulents keep dying in simple terms I can understand. Give me a step-by-step care routine that’s impossible to mess up. Don’t use any complicated plant terminology or suggest expensive equipment.”
The Response Quality Spectrum: Same Question, Different Results
To understand the dramatic impact of prompt quality, consider this comparison across different prompting approaches for the same task:
Basic Prompt: “Write a product description for a coffee maker.”
Result: Generic, features-focused copy that could apply to any appliance
Improved Prompt: “Write a 3-5 sentence product description for the BrewMaster Pro, a $299 smart coffee maker targeting tech-savvy professionals who value convenience and quality. Focus on time-saving benefits and premium coffee experience.”
Result: Targeted, benefit-oriented copy that speaks to specific customer needs
Optimized Prompt: “You are a senior copywriter for premium kitchen appliances. Write a 3-5 sentence product description for the BrewMaster Pro ($299 smart coffee maker) targeting affluent tech professionals. Include: morning routine optimization, app connectivity benefits, and premium coffee quality. Use confident, sophisticated tone. Avoid technical jargon. Ensure each sentence highlights a distinct value proposition.”
Result: Compelling, customer-focused copy that drives purchase intent
The progression from basic to optimized represents not just better wording, but a systematic approach that leverages the model’s full capabilities while maintaining consistency and relevance.
Quick-Hack Prompting Principles
Academic research has identified 26 evidence-based principles that consistently improve prompt performance across different models and tasks. The most impactful include:
Chain-of-Thought Integration: Adding “think step-by-step” improves mathematical and logical reasoning accuracy by 50%. This works because it activates the model’s reasoning pathways rather than jumping directly to conclusions.
Emotional Context: Including phrases like “this is important to my career” increases accuracy by 20% in some contexts. This leverages the model’s training on human communication patterns where importance signals lead to more careful processing.
Leading Words: Starting code generation prompts with “import” or SQL prompts with “SELECT” improves syntax accuracy by providing clear pattern initiation signals.
Output Primers: Ending prompts with the beginning of the desired output (like “1.” for lists) improves format adherence by 75%.
Question Elicitation: Allowing the model to ask clarifying questions before responding improves output quality by 100% for complex tasks, as it can gather missing information rather than making assumptions.
The Bottom Line: You’re the Director, Not the Audience
Think of AI like a really smart friend who’s eager to help but needs clear directions. The difference between “Hey, help me with something” and “Hey, I need help planning a surprise birthday party for my wife who loves gardening and hates surprises, with 15 guests, in our small apartment, with a $300 budget” is the difference between getting “Uh, maybe some balloons?” and getting a detailed party plan with timeline, shopping list, and contingency ideas.
The creativity breakthrough isn’t about the AI getting smarter—it’s about you learning to ask better questions. Once you know the tricks, every conversation with AI becomes more useful, more interesting, and way less frustrating.
So next time you’re about to type a simple request, pause and think: “How can I make this more specific, more personal, or ask for multiple options?” Your AI conversations will never be the same


